Sulforaphane increases brain glutathione: relevance in autism, TBI, brain aging | Rhonda Patrick
Enter your email to get our 15-page guide to sprouting broccoli and learn about the science of chemoprotective compount sulforaphane.
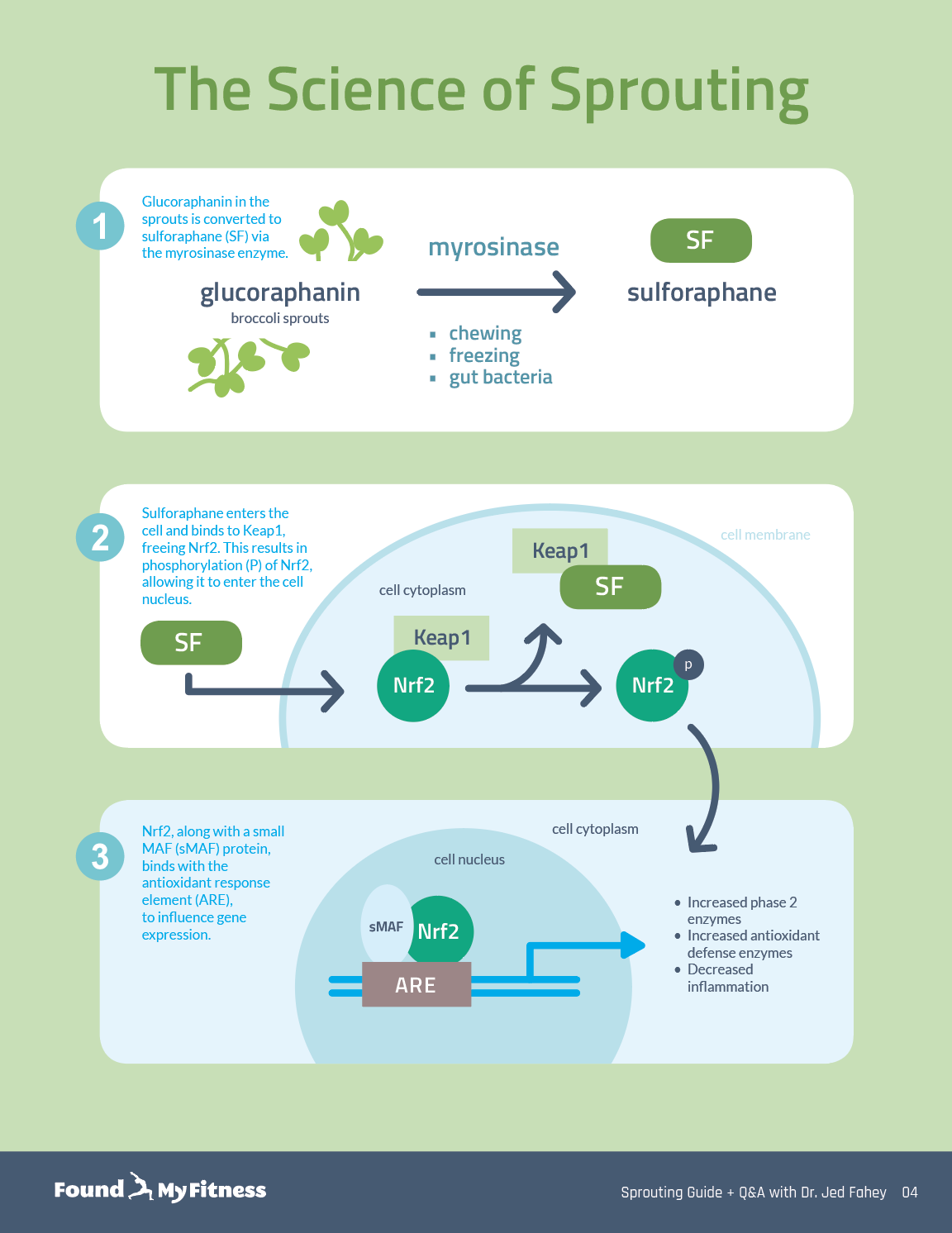
Broccoli sprouts are concentrated sources of sulforaphane, a type of isothiocyanate. Damaging broccoli sprouts – when chewing, chopping, or freezing – triggers an enzymatic reaction in the tiny plants that produces sulforaphane.
Get the full length version of this episode as a podcast.
This episode will make a great companion for a long drive.
Oxidative stress plays a critical role in aging, traumatic brain injury, and autism. Recent clinical evidence suggests that sulforaphane raises levels of the potent antioxidant glutathione in the plasma and brain. In two independent studies, sulforaphane showed promising outcomes, with children and adolescents exhibiting marked reductions in autistic behavior. In this clip, Dr. Rhonda Patrick describes advances in sulforaphane research that are particularly relevant to the brain.
Attend Monthly Q&As with Rhonda
Support our work

The FoundMyFitness Q&A happens monthly for premium members. Attend live or listen in our exclusive member-only podcast The Aliquot.
Sulforaphane News
- Sulforaphane-rich broccoli sprout extract modestly lowers fasting blood sugar in some people with prediabetes, perhaps due to variations in gut microbiota and individual metabolic traits.
- Sulforaphane, derived from broccoli, activates Nrf2, mitigating age-related skin changes and boosting the antioxidant defense system in mice.
- Sulforaphane from broccoli sprouts shows promise in preventing Alzheimer's disease – boosting memory and enhancing mitochondrial function in mice.
- Breathwork enhances endogenous antioxidant enzyme activity to counter oxidative stress.
- Every 1 percent drop in body weight slows brain aging by nearly nine months, highlighting the substantial, and often overlooked, neuroprotective benef
















































