Joe Rogan Experience #1178 - Dr. Rhonda Patrick
The BDNF Protocol Guide
An essential checklist for cognitive longevity — filled with specific exercise, heat stress, and omega-3 protocols for boosting BDNF. Enter your email, and we'll deliver it straight to your inbox.
Dr. Rhonda Patrick makes her eighth appearance on the Joe Rogan Experience.
A few of the topics and studies mentioned in this episode include...
-
BPA in plastic bottles is a potential endocrine disruptor. Study.
-
BPA has diverse effects on human health, including endocrine, reproductive, and transgenerational epigenetic effects. Study.
-
BPA alters insulin sensitivity. Study.
-
BPA interferes with in vitro fertilization. Study.
-
BPA transfers across placenta: Study.
-
BPA leaches out of baby bottles with repeated use. Study.
-
Carnivore diet
-
People consume less when following a low carb, high protein diet. Study.
-
Diet monotony induces food habituation and decreases food intake. Study.
-
Fasting-mimicking diet and ketogenic diet improve symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Study.
-
Profound changes in gut microbiome occur with intermittent fasting. Study.
-
Minocycline, a type of antibiotic, relieved symptoms of multiple sclerosis due to alterations in gut microbiome. Study.
-
The gut microbiome plays key roles in human health and disease. Study.
-
When people change from a high fiber to a high protein diet, their gut microbiome undergoes rapid and dramatic change. Study.
-
“Putrefactive” bacteria in gut metabolize amino acids and are linked with increased risk of colon cancer. Study.
-
Fasting favorably alters the gut microbiome. Study.
-
Organs shrink during fasting and then regrow after refeeding. Study.
-
Fasting stresses healthy cells so they increase their stress-response pathways, including heat shock proteins, antioxidant production, and anti-inflammatory. Study.
-
Ketogenic diet improves symptoms in people with autoimmune disease. Study.
-
The placebo and nocebo effect has a genetic basis. Study.
-
Placebo/nocebo effect seen in gluten sensitivity studies. Study.
-
Dietary fish oil increases dopamine production in brain. Study.
-
How the RDAs - Recommended Dietary Allowances - are set: randomized controlled and non-randomized controlled trials, and depletion-repletion, balance, cross-sectional, and case studies. Study.
-
Carnivore diet deficiency: Vitamin C
-
Vitamin C and glucose use different transporters to enter cells. Study
-
RDA for vitamin C based on depletion-repletion studies. Study.
-
There’s a lot of biological variation in vitamin C needs. Study.
-
Carnivore diet deficiency: Vitamin E
-
RDA for vitamin E based on its ability to maintain cell integrity. Study.
-
Men on low vitamin E diet showed hemolysis of their red blood cells after 2.5 years. Study.
-
Inadequate folate causes double-stranded breaks in DNA. Study.
-
Lack of consumer tests available for measuring DNA damage accurately
-
Phytochemicals as activators of beneficial stress response and evolutionary context.
-
Sulforaphane
-
Broccoli sprouts have 10 to 100 times more sulforaphane than mature broccoli. Isothiocyanate facts.
-
Sulforaphane promotes urinary excretion of benzene and acrolein, compounds in air pollution. Study.
-
Sulforaphane activates Phase II detoxification enzymes and deactivates Phase I biotransformation enzymes, which can convert compounds to carcinogens. Study.
-
Sulforaphane lowers biomarker for prostate cancer 86%. Study.
-
Sulforaphane in Brussels sprouts increases antioxidant compound glutathione. Study.
-
Sulforaphane in brussels sprouts decreases oxidative DNA damage. Study.
-
Sulforaphane increases antioxidant compound glutathione in human brain. Study.
-
Major changes in diet can alter the gut microbiome and temporarily cause discomfort
-
Fasting and the fasting-mimicking diet
-
Types of Alzheimer’s disease and current status of research
-
-
APOE4 as a genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease
-
Amyloid plaques in brain are cleared away during sleep. Study.
-
People who have APOE4 have a reduced efficiency of amyloid clearance. Study.
-
Faulty DHA transport system in brains of people with APOE4 can be bypassed with phospholipid form of DHA. Study.
-
Fish oil lowered cardiovascular disease risk by ~30%. Study.
-
-
Ketones and Ketosis
-
Sulforaphane supplementation
-
Parenthood
-
Health benefits of heat stress
-
Single episode of sauna use improves vascular compliance (blood vessels’ ability to contract and expand), reduces blood pressure, and decreases CRP. Study.
-
Sauna stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle. Study.
-
Sauna use may reduce a chronic inflammatory state by reducing inflammatory cytokines. Study.
-
Sauna use before working out reduces delayed-onset muscle soreness associated with exercise. Study.
-
Increasing core body temperature decreases symptoms of depression. Dr. Raison study.
-
Taking NSAIDs before working out blunts some of the benefits derived from exercise. Study.
-
Effects of sensory deprivation
Scientists mentioned
- Charles Raison
- Valter Longo
- Jed Fahey
- Mark Levine
- Alessio Fasano
-
BPA in plastic bottles is a potential endocrine disruptor. Study.
-
BPA has diverse effects on human health, including endocrine, reproductive, and transgenerational epigenetic effects. Study.
-
BPA alters insulin sensitivity. Study.
-
BPA interferes with in vitro fertilization. Study.
-
BPA transfers across placenta: Study.
-
BPA leaches out of baby bottles with repeated use. Study.
-
Carnivore diet
-
People consume less when following a low carb, high protein diet. Study.
-
Diet monotony induces food habituation and decreases food intake. Study.
-
Fasting-mimicking diet and ketogenic diet improve symptoms of multiple sclerosis. Study.
-
Profound changes in gut microbiome occur with intermittent fasting. Study.
-
Minocycline, a type of antibiotic, relieved symptoms of multiple sclerosis due to alterations in gut microbiome. Study.
-
The gut microbiome plays key roles in human health and disease. Study.
-
When people change from a high fiber to a high protein diet, their gut microbiome undergoes rapid and dramatic change. Study.
-
“Putrefactive” bacteria in gut metabolize amino acids and are linked with increased risk of colon cancer. Study.
-
Fasting favorably alters the gut microbiome. Study.
-
Organs shrink during fasting and then regrow after refeeding. Study.
-
Fasting stresses healthy cells so they increase their stress-response pathways, including heat shock proteins, antioxidant production, and anti-inflammatory. Study.
-
Ketogenic diet improves symptoms in people with autoimmune disease. Study.
-
The placebo and nocebo effect has a genetic basis. Study.
-
Placebo/nocebo effect seen in gluten sensitivity studies. Study.
-
Dietary fish oil increases dopamine production in brain. Study.
-
How the RDAs - Recommended Dietary Allowances - are set: randomized controlled and non-randomized controlled trials, and depletion-repletion, balance, cross-sectional, and case studies. Study.
-
Carnivore diet deficiency: Vitamin C
-
Vitamin C and glucose use different transporters to enter cells. Study
-
RDA for vitamin C based on depletion-repletion studies. Study.
-
There’s a lot of biological variation in vitamin C needs. Study.
-
Carnivore diet deficiency: Vitamin E
-
RDA for vitamin E based on its ability to maintain cell integrity. Study.
-
Men on low vitamin E diet showed hemolysis of their red blood cells after 2.5 years. Study.
-
Inadequate folate causes double-stranded breaks in DNA. Study.
-
Lack of consumer tests available for measuring DNA damage accurately
-
Phytochemicals as activators of beneficial stress response and evolutionary context.
-
Sulforaphane
-
Broccoli sprouts have 10 to 100 times more sulforaphane than mature broccoli. Isothiocyanate facts.
-
Sulforaphane promotes urinary excretion of benzene and acrolein, compounds in air pollution. Study.
-
Sulforaphane activates Phase II detoxification enzymes and deactivates Phase I biotransformation enzymes, which can convert compounds to carcinogens. Study.
-
Sulforaphane lowers biomarker for prostate cancer 86%. Study.
-
Sulforaphane in Brussels sprouts increases antioxidant compound glutathione. Study.
-
Sulforaphane in brussels sprouts decreases oxidative DNA damage. Study.
-
Sulforaphane increases antioxidant compound glutathione in human brain. Study.
-
Major changes in diet can alter the gut microbiome and temporarily cause discomfort
-
Fasting and the fasting-mimicking diet
-
Types of Alzheimer’s disease and current status of research
-
-
APOE4 as a genetic risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease
-
Amyloid plaques in brain are cleared away during sleep. Study.
-
People who have APOE4 have a reduced efficiency of amyloid clearance. Study.
-
Faulty DHA transport system in brains of people with APOE4 can be bypassed with phospholipid form of DHA. Study.
-
Fish oil lowered cardiovascular disease risk by ~30%. Study.
-
-
Ketones and Ketosis
-
Sulforaphane supplementation
-
Parenthood
-
Health benefits of heat stress
-
Single episode of sauna use improves vascular compliance (blood vessels’ ability to contract and expand), reduces blood pressure, and decreases CRP. Study.
-
Sauna stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle. Study.
-
Sauna use may reduce a chronic inflammatory state by reducing inflammatory cytokines. Study.
-
Sauna use before working out reduces delayed-onset muscle soreness associated with exercise. Study.
-
Increasing core body temperature decreases symptoms of depression. Dr. Raison study.
-
Taking NSAIDs before working out blunts some of the benefits derived from exercise. Study.
-
Effects of sensory deprivation
This transcript is reserved for members.
FoundMyFitness Members get access to exclusive content not available anywhere else, including a transcript of this episode.
You wouldn't believe how cool being a premium member of the world's best cross-disciplinary science-focused website and podcast really is.
The simplest unsaturated aldehyde, created by the burning of glycerol in animal fat. Acrolein, a toxic, colorless liquid, is a strong irritant for the skin, eyes, and nasal passages of humans. It has a disagreeable, acrid smell, easily recognizable as the odor associated with burning fat.
The primary protein present in human blood plasma. Albumin binds water, minerals, fatty acids, hormones, bilirubin, and many drugs. Its main function is to regulate the oncotic pressure of blood, a form of osmotic pressure exerted by proteins that tends to pull water into the circulatory system.
The death rate from all causes of death for a population in a given time period.
A neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive memory loss, spatial disorientation, cognitive dysfunction, and behavioral changes. The pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease include amyloid-beta plaques, tau tangles, and reduced brain glucose uptake. Most cases of Alzheimer's disease do not run in families and are described as "sporadic." The primary risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer's disease is aging, with prevalence roughly doubling every five years after age 65. Roughly one-third of people aged 85 and older have Alzheimer's. The major genetic risk factor for Alzheimer's is a variant in the apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene called APOE4.
One of three common genetic variants of the APOE (apolipoprotein E) gene. The APOE4 allele, which is present in approximately 10-15% of people, increases the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease and lowers the age of onset. Having one copy of E4 increases risk 2- to 3-fold, while having two copies increases risk as much as 15-fold.
Programmed cell death. Apoptosis is a type of cellular self-destruct mechanism that rids the body of damaged or aged cells. Unlike necrosis, a process in which cells that die as a result of acute injury swell and burst, spilling their contents over their neighbors and causing a potentially damaging inflammatory response, a cell that undergoes apoptosis dies in a neat and orderly fashion – shrinking and condensing, without damaging its neighbors. The process of apoptosis is often blocked or impaired in cancer cells. (May be pronounced “AY-pop-TOE-sis” OR “AP-oh-TOE-sis”.)
A naturally-occurring element found in soil, water, food, and air. Chronic arsenic exposure is associated with the development of several diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. In utero and early childhood exposure to arsenic is associated with poor cognitive development and increased deaths in young adults.
The shrinking or wasting away of cells, organs, or tissues that may occur as part of a disease process, trauma, or aging.
A developmental disorder characterized by impaired social interaction, behavioral problems, and poor communication. Autism typically manifests in early childhood and is slightly more common among boys than girls. In clinical trials, sulforaphane, a compound derived from broccoli and broccoli sprouts, reduces the characteristic behaviors associated with autism.
An immune disorder characterized by an immune response to and subsequent destruction of the body’s own tissue. The causes of autoimmune diseases are not known, but a growing body of evidence suggests they may be due to interactions between genetic and environmental factors. Autoimmune diseases affect approximately 7 percent of the population in the United States and are more common in women than in men. Examples include type 1 diabetes, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis.
An intracellular degradation system involved in the disassembly and recycling of unnecessary or dysfunctional cellular components. Autophagy participates in cell death, a process known as autophagic dell death. Prolonged fasting is a robust initiator of autophagy and may help protect against cancer and even aging by reducing the burden of abnormal cells.
The relationship between autophagy and cancer is complex, however. Autophagy may prevent the survival of pre-malignant cells, but can also be hijacked as a malignant adaptation by cancer, providing a useful means to scavenge resources needed for further growth.
An aromatic hydrocarbon compound produced during the distillation and burning of fossil fuels, such as gasoline. It is also present in the smoke from forest fires, volcanoes, and cigarettes. Benzene is a carcinogen that targets the liver, kidney, lung, heart, and brain and can cause DNA strand breaks, chromosomal damage, and genetic instability.
A chemical produced in the liver via the breakdown of fatty acids. Beta-hydroxybutyrate is a type of ketone body. It can be used to produce energy inside the mitochondria and acts as a signaling molecule that alters gene expression by inhibiting a class of enzymes known as histone deacetylases.
A genus of bacteria known to inhabit the human gut. Bifidobacteria are anaerobic commensal bacteria. They are among the first bacteria to colonize the infant gut and may play critical roles in gut-mediated immune function.
Proteins that provide favorable conditions for the correct folding of other proteins. Newly made proteins usually must fold from a linear chain of amino acids into a three-dimensional form. Group II chaperonins, the variety found in eukaryotic cytosol, are also referred to as CCT, which stands for "chaperonin containing TCP-1."
The extent and rate at which drugs or other substances, such as plant-based dietary compounds, enter the body’s circulation. Bioavailability is influenced by a variety of factors, including dose, the presence of other foods or substances, and interindividual differences in metabolism due to gut absorptive surface and commensal microbial populations.
A highly selective semi-permeable barrier in the brain made up of endothelial cells connected by tight junctions. The blood-brain barrier separates the circulating blood from the brain's extracellular fluid in the central nervous system. Whereas water, lipid-soluble molecules, and some gases can pass through the blood-brain barrier via passive diffusion, molecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function enter via selective transport. The barrier prevents the entry of lipophilic substances that may be neurotoxic via an active transport mechanism.
The practice of long-term restriction of dietary intake, typically characterized by a 20 to 50 percent reduction in energy intake below habitual levels. Caloric restriction has been shown to extend lifespan and delay the onset of age-related chronic diseases in a variety of species, including rats, mice, fish, flies, worms, and yeast.
A substance whose presence is essential for the activity of an enzyme. Many minerals and vitamins are cofactors for enzymes.
Bacteria that are beneficial or at least not harmful to the host, in contrast to pathogenic bacteria where the host derives no benefit and is actively harmed from the relationship. Roughly 100 trillion commensal bacteria live in the human gut. The term commensal comes from Latin and literally means “eating at the same table.”
Complex carbohydrate foods provide vitamins, minerals, and fiber that are important to the health of an individual. As opposed to simple or refined sugars, which do not have the vitamins, minerals, and fiber found in complex and natural carbohydrates. Simple sugars are often called "empty calories" because they have little to no nutritional value.
A variable that is related to one or more of the other variables in a study. A confounding factor can mask an association that exists between variables or demonstrate an association that does not exist. If confounding factors are not measured and considered, the findings of the study may be biased.
In statistics, a confounder (also confounding variable or confounding factor) is a variable that is correlated (directly or inversely) to both the dependent variable and independent variable.
An antioxidant compound produced by the plant Curcuma longa, a member of the ginger family. Curcumin exhibits a wide array of beneficial health effects, including anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-diabetes properties. It is responsible for the bright yellow pigment of turmeric, a type of spice commonly used in Indian food.
A broad category of small proteins (~5-20 kDa) that are important in cell signaling. Cytokines are short-lived proteins that are released by cells to regulate the function of other cells. Sources of cytokines include macrophages, B lymphocytes, mast cells, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells. Types of cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumor necrosis factor.
A general term referring to cognitive decline that interferes with normal daily living. Dementia commonly occurs in older age and is characterized by progressive loss of memory, executive function, and reasoning. Approximately 70 percent of all dementia cases are due to Alzheimer’s disease.
A mood disorder characterized by profound sadness, fatigue, altered sleep and appetite, as well as feelings of guilt or low self-worth. Depression is often accompanied by perturbations in metabolic, hormonal, and immune function. A critical element in the pathophysiology of depression is inflammation. As a result, elevated biomarkers of inflammation, including the proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, are commonly observed in depressed people. Although selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and cognitive behavioral therapy typically form the first line of treatment for people who have depression, several non-pharmacological adjunct therapies have demonstrated effectiveness in modulating depressive symptoms, including exercise, dietary modification (especially interventions that capitalize on circadian rhythms), meditation, sauna use, and light therapy, among others.
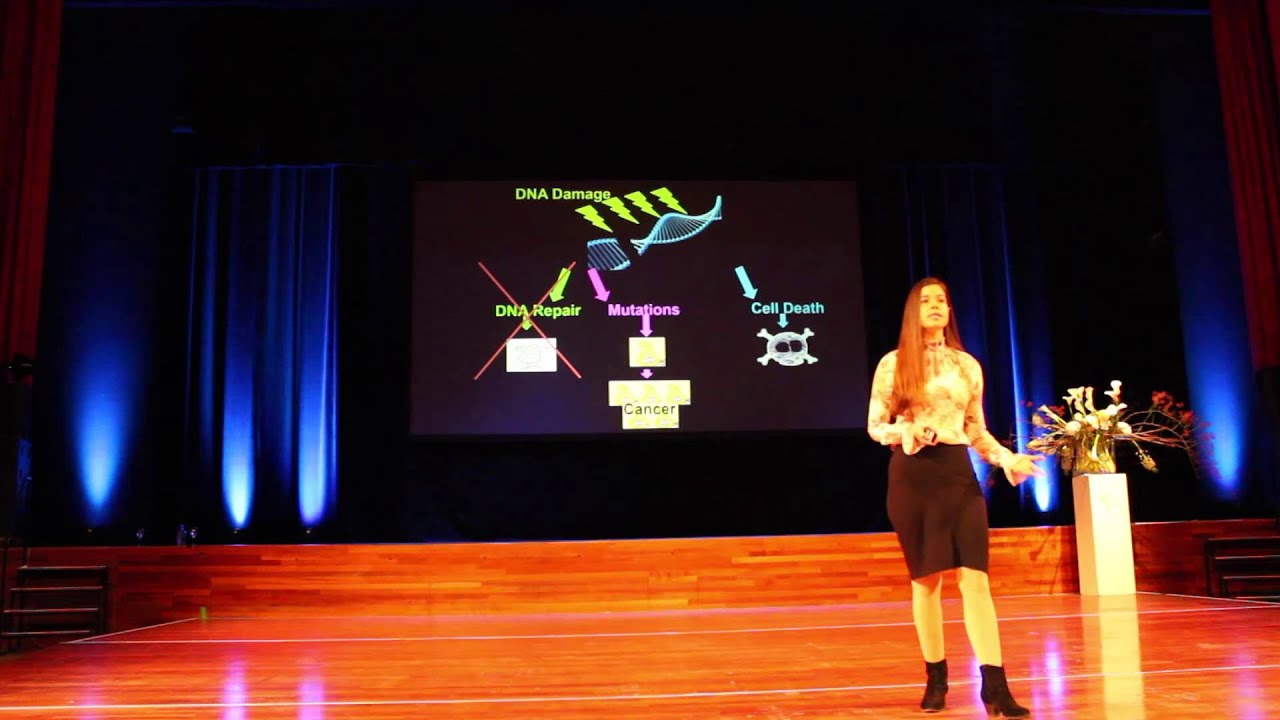
A major contributing factor to aging, cellular senescence, and the development of cancer. Byproducts of both mitochondrial energy production and immune activity are major sources of DNA damage. Additionally, environmental stressors can increase this base level of damage. DNA damage can be mitigated by cellular repair processes; however, the effectiveness of these processes may be influenced by the availability of dietary minerals, such as magnesium, and other dietary components, which are needed for proper function of repair enzymes.
A neurotransmitter best known for its role in motor, motivation, and pleasure control. Dopamine also functions as a paracrine (cell-to-cell) hormone in other parts of the body. It is derived from tyrosine and is the precursor to norepinephrine and epinephrine. Some evidence suggests that dopamine may also be involved in pain modulation.
A potent endogenous opioid peptide. Dynorphin acts on the kappa-opioid receptor and is associated with a transient feeling of dysphoria. It has many different physiological actions, depending upon its site of production, and is involved in addiction, temperature regulation, appetite, circadian rhythm, pain, stress, and depression. Dynorphin may also be involved in the body’s thermoregulatory response to hyperthermia.[1]
System of glands regulating the body through the production of hormones. The endocrine system's effects are slow to initiate, and prolonged in their response, lasting from a few hours up to weeks. In contrast, the nervous system sends information very quickly, and responses are generally short lived.
The single layer of cells that lines the interior of the blood and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium participates in blood flow, platelet aggregation, and vascular tone. It also regulates inflammation, immune function, and angiogenesis. Endothelial dysfunction is a systemic pathological condition broadly defined as an imbalance between vasodilating and vasoconstricting substances produced by (or acting on) the endothelium. It is a robust predictor of heart attack and stroke risk.
A molecule composed of carboxylic acid with a long hydrocarbon chain that is either saturated or unsaturated. Fatty acids are important components of cell membranes and are key sources of fuel because they yield large quantities of ATP when metabolized. Most cells can use either glucose or fatty acids for this purpose.
Flavonoid are widely distributed in plants, fulfilling many functions. Flavonoids have been shown to have a wide range of biological and pharmacological activities in animal, human, and in-vitro studies. Examples include anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-cancer, and anti-diarrheal activities.
A type of water-soluble B-vitamin, also called vitamin B9. Folate is critical in the metabolism of nucleic acid precursors and several amino acids, as well as in methylation reactions. Severe deficiency in folate can cause megaloblastic anemia, which causes fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. Certain genetic variations in folate metabolism, particularly those found in the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene influences folate status. Inadequate folate status during early pregnancy increases the risk of certain birth defects called neural tube defects, or NTDs, such as spina bifida, anencephaly, and other similar conditions. Folate deficiency and elevated concentrations of homocysteine in the blood are associated with increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Low folate status and/or high homocysteine concentrations are associated with cognitive dysfunction in aging (from mild impairments to dementia). The synthetic form of folate is called folic acid. Sources of folate include most fruits and vegetables, especially green leafy vegetables.
A hormone produced in the gut that signals hunger. Ghrelin acts on cells in the hypothalamus to stimulate appetite, increase food intake, and promote growth. Ghrelin’s effects are opposed by leptin, the “satiety hormone.” Sleep deprivation increases ghrelin levels and feelings of hunger, which can lead to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction.
A glucosinolate (see definition) found in certain cruciferous vegetables, including broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and mustard. Glucoraphanin is hydrolyzed by the enzyme myrosinase to produce sulforaphane, an isothiocyanate compound that has many beneficial health effects in humans.
A survival mechanism the brain relies on during starvation. Glucose sparing occurs when the body utilizes fatty acids as its primary fuel and produces ketone bodies. The ketone bodies cross the blood-brain barrier and are used instead of glucose, thereby “sparing” glucose for use in other metabolic pathways, such as the pentose-phosphate pathway, which produces NADPH. NADPH is essential for the production of glutathione, one of the major antioxidants used in the body and brain.
An antioxidant compound produced by the body’s cells. Glutathione helps prevent damage from oxidative stress caused by the production of reactive oxygen species.
A complex mixture of hundreds of related but distinct proteins, mainly gliadin and glutenin, found in wheat. Similar proteins are found in rye (secalin), barley (hordein), and oats (avenin), are evolutionarily connected, and are collectively referred to as “gluten.” Gluten proteins, which are highly resistant to hydrolysis in the human gut, can give rise to pathogenic peptides, which may promote the development of celiac disease or wheat allergy in genetically predisposed people. The global prevalence of celiac disease is 1%, with a statistical range of probability of 0.5–1.26% in the general population in Europe and the US.
An estimate of the effects of carbohydrate consumption using the glycemic index (GI) while taking into account the amount of carbohydrate that is consumed. In other words, glycemic load is a GI-weighted measure of carbohydrate content that is defined as the grams of available carbohydrate in the food, multiplied by the food's GI.
A family of proteins produced by cells in response to exposure to stressful conditions. Heat shock proteins are expressed in response to heat as well as exposure to cold and UV light, and during wound healing and tissue remodeling. Many heat shock proteins function as chaperones by stabilizing new proteins to ensure correct folding or by helping to refold proteins that were damaged by cell stress. A 30-minute 73ºC sauna session in healthy young adults has been shown to cause a robust and sustained increase in the production of heat shock proteins for up to 48 hours afterward.[1]
- ^ Shields, Richard K; Iguchi, Masaki; Littmann, Andrew E.; Chang, Shuo-Hsiu; Wester, Lydia A.; Knipper, Jane S. (2012). Heat Stress And Cardiovascular, Hormonal, And Heat Shock Proteins In Humans Journal Of Athletic Training 47, 2.
An amino acid present in the blood. Homocysteine is produced during the metabolism of methionine. Abnormalities in methionine metabolism can lead to elevated homocysteine levels, a condition called hyperhomocysteinemia. Elevated homocysteine levels can contribute to arterial plaque formation and increase the risk of clot formation. Some evidence suggests that elevated homocysteine levels double the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Homocysteine levels vary according to dietary intake, with highest levels associated with consumption of animal protein. Variants in the genes that encode for the enzymes that metabolize homocysteine, specifically MTHFR, or methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, markedly increase the risk of developing a wide array of diseases, including cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. High intake of dietary folate (present in leafy greens and other fruits and vegetables) can modulate the harmful effects associated with MTHFR.
A critical element of the body’s immune response. Inflammation occurs when the body is exposed to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. It is a protective response that involves immune cells, cell-signaling proteins, and pro-inflammatory factors. Acute inflammation occurs after minor injuries or infections and is characterized by local redness, swelling, or fever. Chronic inflammation occurs on the cellular level in response to toxins or other stressors and is often “invisible.” It plays a key role in the development of many chronic diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
A peptide hormone secreted by the beta cells of the pancreatic islets cells. Insulin maintains normal blood glucose levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells; regulating carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism; and promoting cell division and growth. Insulin resistance, a characteristic of type 2 diabetes, is a condition in which normal insulin levels do not produce a biological response, which can lead to high blood glucose levels.
A trace mineral that is essential for human health. Iodine is necessary for normal thyroid and immune function.
Byproduct of a reaction between two compounds (glucosinolates and myrosinase) that are found in cruciferous vegetables. Isothiocyanates inhibit phase I biotransformation enzymes, a class of enzymes that transform procarcinogens into their active carcinogenic state. Isothiocyanates activate phase II detoxification enzymes, a class of enzymes that play a protective role against DNA damage caused by reactive oxygen species and carcinogens. Examples of phase II enzymes include UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, sulfotransferases, N-acetyltransferases, glutathione S-transferases, and methyltransferases.
A diet that causes the body to oxidize fat to produce ketones for energy. A ketogenic diet is low in carbohydrates and high in proteins and fats. For many years, the ketogenic diet has been used in the clinical setting to reduce seizures in children. It is currently being investigated for the treatment of traumatic brain injury, Alzheimer's disease, weight loss, and cancer.
Molecules (often simply called “ketones”) produced by the liver during the breakdown of fatty acids. Ketone production occurs during periods of low food intake (fasting), carbohydrate restrictive diets, starvation, or prolonged intense exercise. There are three types of ketone bodies: acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone. Ketone bodies are readily used as energy by a diverse array of cell types, including neurons.
Lactate is thought to participate in a sort of "lactate shuttle" where, after being produced in muscle from exercise, it is transported in to tissues like the heart, and brain, where it is used as an energy source. Lactate is one of many molecules that falls under a loose group of molecules referred to as exerkines, a broad group of exercise-induced hormonal-like factors. Evidence suggests that lactate is the preferred fuel of the brain. Additionally, rodent studies suggest that lactate mediates some of the benefits of exercise on learning and memory via inducing neuronal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) expression.[1] In clinical studies, lactate shows promise as a treatment for inflammatory conditions including traumatic brain injury and as a means to deliver fuel to working muscles.
- ^ Helge, Jørn Wulff; Moritz, Thomas; Morville, Thomas; Clemmensen, Christoffer; Dela, Flemming (2020). Plasma Metabolome Profiling Of Resistance Exercise And Endurance Exercise In Humans Cell Reports 33, 13.
A class of proteins present in many edible plants, such as grains or legumes. Lectins are carbohydrate-binding molecules. They have been referred to as antinutrients for their ability to impair absorption of some nutrients. Many lectins possess hemagglutinin properties, which means they can bind to blood cells and cause them to aggregate. Cooking typically denatures lectins in foods.
A hormone produced primarily by adipocytes (fat cells) that signals a feeling of satiety, or fullness, after a meal. Leptin acts on cells in the hypothalamus to reduce appetite and subsequent food intake. Leptin’s effects are opposed by ghrelin, the “hunger hormone.” Both acute and chronic sleep deprivation decrease leptin levels.
A family of eicosanoid inflammatory mediators produced by leukocytes (a type of white blood cell).
A group of blood tests that measures the amount of lipids (fats) in a person’s blood. Typical elements of a lipid panel (also known as a lipid profile) include total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Increasingly, evidence suggests that blood tests that assess predominant particle size may also be an important factor in interpreting the overall impact of HDL and LDL values.
The collection of genomes of the microorganisms in a given niche. The human microbiome plays key roles in development, immunity, and nutrition. Microbiome dysfunction is associated with the pathology of several conditions, including obesity, depression, and autoimmune disorders such as type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, muscular dystrophy, multiple sclerosis, and fibromyalgia.
Vitamins and minerals that are required by organisms throughout life in small quantities to orchestrate a range of physiological functions. The term micronutrients encompasses vitamins, minerals, essential amino acids, essential fatty acids.
Tiny organelles inside cells that produce energy in the presence of oxygen. Mitochondria are referred to as the "powerhouses of the cell" because of their role in the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Mitochondria are continuously undergoing a process of self-renewal known as mitophagy in order to repair damage that occurs during their energy-generating activities.
The process by which new mitochondria are made inside cells. Many factors can activate mitochondrial biogenesis including exercise, cold shock, heat shock, fasting, and ketones. Mitochondrial biogenesis is regulated by the transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, or PGC-1α.
A mucopolysaccharide or glycoprotein that is the chief constituent of mucus secreted by the epithelial cells lining the gut in order to produce a barrier preventing infection by microorganisms inhabiting the gut.
A family of enzymes whose sole known substrates are glucosinolates. Myrosinase is located in specialized cells within the leaves, stems, and flowers of cruciferous plants. When the plant is damaged by insects or eaten by humans, the myrosinase is released and subsequently hydrolyzes nearby glucosinolate compounds to form isothiocyanates (see definition), which demonstrate many beneficial health effects in humans. Microbes in the human gut also produce myrosinase and can convert non-hydrolyzed glucosinolates to isothiocyanates.
A type of white blood cell, also known as a granulocyte. Neutrophils are the most abundant form of blood cell, comprising approximately 60 percent of total cells. They ingest, kill, and digest microbial pathogens, and are the first cells recruited to acute sites of injury. Neutrophils can infiltrate brain structures, driving inflammation and increasing the risk for neurodegenerative disorders, such as Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease.
A substance produced in the brain. Norepinephrine acts as a hormone and neurotransmitter and is best known for its role in the body’s “fight or flight” response to stress. Its role as a neurotransmitter has been exploited as a molecular target for a class of drugs known as norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, which were developed for the purpose of treating disorders ranging from ADHD to narcolepsy and depression. Norepinephrine also plays a role in converting white adipose tissue into brown adipose tissue via an uncoupling protein 1 (UCP-1) mediated mechanism.
A type of polyunsaturated fat that is essential for human health. Omega-3 fatty acids influence cell membrane integrity and affect the function of membrane-bound cellular receptors. They participate in pathways involved in the biosynthesis of hormones that regulate blood clotting, contraction and relaxation of artery walls, and inflammation. They have been shown to help prevent heart disease and stroke, may help control lupus, eczema, and rheumatoid arthritis, and may play protective roles in cancer and other conditions. Omega-3 fatty acids include alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). ALA is found mainly in plant oils such as flaxseed, soybean, and canola oils. DHA and EPA are found in fish and other seafood. The human body can convert some ALA into EPA and then to DHA, but the efficiency of the process varies between individuals.
A chemical reaction in which an atom, molecule, or ion loses one or more electrons. Oxidation of biological molecules is associated with oxidative stress, a key driver of many chronic diseases.
A result of oxidative metabolism, which causes damage to DNA, lipids, proteins, mitochondria, and the cell. Oxidative stress occurs through the process of oxidative phosphorylation (the generation of energy) in mitochondria. It can also result from the generation of hypochlorite during immune activation.
A diet based mainly on foods presumed to be available to paleolithic humans. It includes vegetables, fruits, nuts, roots, meat, and organ meats while excluding foods such as dairy products, grains, refined sugar, legumes, and other processed foods.
In general, anything that can produce disease. Typically, the term is used to describe an infectious agent such as a virus, bacterium, prion, fungus, or other microorganism.
A class of detoxification enzymes that play important roles in the metabolic inactivation and/or biotransformation of endogenous compounds, xenobiotics, and drugs so that they are more easily excreted from the body. Phase II enzymes are typically transferases, such as UDP-glucuronosyltransferases, sulfotransferases, N-acetyltransferases, glutathione S-transferases, and methyltransferases. They are involved in glutathione synthesis, reactive oxygen species elimination, detoxification, drug excretion, and NADPH synthesis. Reduced phase II enzyme capacity or activity can lead to toxic effects and increased risk of certain diseases, including cancer.
The observable physical characteristics of an organism. Phenotype traits include height, weight, metabolic profile, and disease state. An individual’s phenotype is determined by both genetic and environmental factors.
A class of chemical compounds produced in plants in response to stressors. Polyphenols contribute to the bitterness, astringency, color, flavor, and fragrance of many fruits and vegetables. They often serve as deterrents to insect or herbivore consumption. When consumed in the human diet, polyphenols exert many health benefits and may offer protection against development of cancers, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, osteoporosis, and neurodegenerative diseases. Dietary sources of polyphenols include grapes, apples, pears, cherries, and berries, which provide as much as 200 to 300 mg polyphenols per 100 grams fresh weight.
The area of the brain located in the front portion of the frontal lobe, just behind the area commonly known as the forehead. The prefrontal cortex is involved in a variety of higher cognitive functions and behaviors such as executive function and expression of appropriate social behavior.
A group of lipid-signaling molecules that have diverse hormone-like effects. Prostaglandins play roles in inflammation, vasoconstriction or vasodilation, aggregation or disaggregation of platelets, calcium movement, cell growth, and thermoregulation. Prostaglandins are produced in many places throughout the human body.
A polyphenolic compound produced in plants in response to injury or pathogenic attack from bacteria or fungi. Resveratrol exerts a diverse array of biological effects, including antitumor, antioxidant, antiviral, and hormonal activities. It activates sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), an enzyme that deacetylates proteins and contributes to cellular regulation (including autophagy). Dietary sources of resveratrol include grapes, blueberries, raspberries, and mulberries.
Resveratrol Autophagy ↑ Deacetylases (especially SIRT1) → ↓ Protein Acetylation → Autophagy
A mental disorder characterized by abnormal social behavior and failure to understand what is real. Common symptoms include false beliefs, unclear or confused thinking, hearing voices that others do not, reduced social engagement and emotional expression, and a lack of motivation. People with schizophrenia often have additional mental health problems such as anxiety disorders, major depressive illness, or substance use disorders.
A disease caused by vitamin C deficiency. Scurvy is characterized by bleeding, swollen gums, poor wound healing, joint pain, and bruising. Clinical features of scurvy appear in a person in as little as 84 to 97 days of vitamin C depletion. As scurvy progresses, a person might experience shortness of breath, dry eyes, joint swelling, weakness, fatigue, and depression.
A small molecule that functions as both a neurotransmitter and a hormone. Serotonin is produced in the brain and gut and facilitates the bidirectional communication between the two. It regulates many physiological functions, including sleep, appetite, mood, thermoregulation, and others. Many antidepressants are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which work by preventing the reabsorption of serotonin, thereby increasing extracellular levels of the hormone.
A class of drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels by blocking the production of an enzyme in the liver called hydroxy-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA reductase). Taking statins may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease in some people. Although statins are generally well tolerated, as many as 10 – 20 percent of people taking the drugs experience complications, including myopathy (muscle damage), liver damage, and cognitive problems, including issues with forgetfulness, memory loss, and confusion.
A cell that has the potential to develop into different types of cells in the body. Stem cells are undifferentiated, so they cannot do specific functions in the body. Instead, they have the potential to become specialized cells, such as muscle cells, blood cells, and brain cells. As such, they serve as a repair system for the body. Stem cells can divide and renew themselves over a long time. In 2006, scientists reverted somatic cells into stem cells by introducing Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and cMyc (OSKM), known as Yamanaka factors.[1]
- ^ Takahashi, Kazutoshi; Yamanaka, Shinya (2006). Induction Of Pluripotent Stem Cells From Mouse Embryonic And Adult Fibroblast Cultures By Defined Factors Cell 126, 4.
An isothiocyanate compound derived from cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, and mustard. Sulforaphane is produced when the plant is damaged when attacked by insects or eaten by humans. It activates cytoprotective mechanisms within cells in a hormetic-type response. Sulforaphane has demonstrated beneficial effects against several chronic health conditions, including autism, cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and others.
The junction between one neuron and another or a gland or muscle cell. Synapses are critical elements in the transmission of nerve signals. Their formation is necessary for the establishment and maintenance of the brain’s neuronal network and the precision of its circuitry.
Abnormal aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau, a protein found in the brain. Tau tangles are associated with traumatic brain injury and chronic traumatic encephalopathy and are one of the defining characteristics of Alzheimer’s disease. They inhibit normal brain function, and the degree of cognitive impairment in diseases such as Alzheimer’s is significantly correlated with their presence.
An enzyme that extends the telomeres of chromosomes. Telomerase adds specific nucleotide sequences to the ends of existing chromosomes. Telomerase activity is highly regulated during development, and its activity is at an almost undetectable level of activity in fully developed cells. This lack of activity causes the cell to age. If telomerase is activated in a cell, the cell will continue to grow and divide, or become "immortal," which is important to both aging and cancer. Telomerase enzyme activity has been detected in more than 90 percent of human cancers.
Distinctive structures comprised of short, repetitive sequences of DNA located on the ends of chromosomes. Telomeres form a protective “cap” – a sort of disposable buffer that gradually shortens with age – that prevents chromosomes from losing genes or sticking to other chromosomes during cell division. When the telomeres on a cell’s chromosomes get too short, the chromosome reaches a “critical length,” and the cell stops dividing (senescence) or dies (apoptosis). Telomeres are replenished by the enzyme telomerase, a reverse transcriptase.
Theory proposed by Dr. Bruce Ames which proposes that when the body is deficient in a micronutrient it will allocate its scarce supply to enzymes necessary for short-term survival and reproduction at the cost of long-term survival enzymes. This may result in the acceleration of the aging process.
A molecule composed of a glycerol molecule bound to three fatty acids. Triglycerides are the primary component of very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL). They serve as a source of energy. Triglycerides are metabolized in the intestine, absorbed by intestinal cells, and combined with cholesterol and proteins to form chylomicrons, which are transported in lymph to the bloodstream.
An essential amino acid. Tryptophan plays key roles in the biosynthesis of proteins and is a precursor to several molecules with physiological significance, including melatonin, niacin, and the neurotransmitter serotonin. Inflammation causes tryptophan to be reallocated from serotonin synthesis to that of kynurenine, which then converts to the neurotoxin quinolinic acid, leading to depression. Dietary sources of tryptophan include most protein-based foods, such as meat, beans, or nuts.
A metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar and insulin resistance. Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition and is typically associated with overweight and low physical activity. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, and impaired healing. Long-term complications from poorly controlled type 2 diabetes include heart disease, stroke, diabetic retinopathy (and subsequent blindness), kidney failure, and diminished peripheral blood flow which may lead to amputations.
A potent water-soluble antioxidant found in citrus fruits. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in tissue repair, neurotransmission, and immune system function. Also known as ascorbic acid.
A fat-soluble vitamin. Vitamin E is the collective name for a group of eight fat-soluble compounds (alpha-, beta-, gamma-, & delta-tocopherol and alpha-, beta-, gamma-, & delta-tocotrienol) with distinctive antioxidant activities. Of these eight, only alpha- (α-) tocopherol meets human requirements. Vitamin E serves as an antioxidant that breaks the chain reaction formation of reactive free radicals. In doing so it becomes oxidized and loses its antioxidant capacity. Vitamin E also protects LDL from oxidation and maintains the integrity of cell membranes throughout the body. Dietary sources of vitamin E include nuts, seeds, eggs, and fatty fish, such as salmon.
Hear new content from Rhonda on The Aliquot, our member's only podcast

Listen in on our regularly curated interview segments called "Aliquots" released every week on our premium podcast The Aliquot. Aliquots come in two flavors: features and mashups.
- Hours of deep dive on topics like fasting, sauna, child development surfaced from our enormous collection of members-only Q&A episodes.
- Important conversational highlights from our interviews with extra commentary and value. Short but salient.